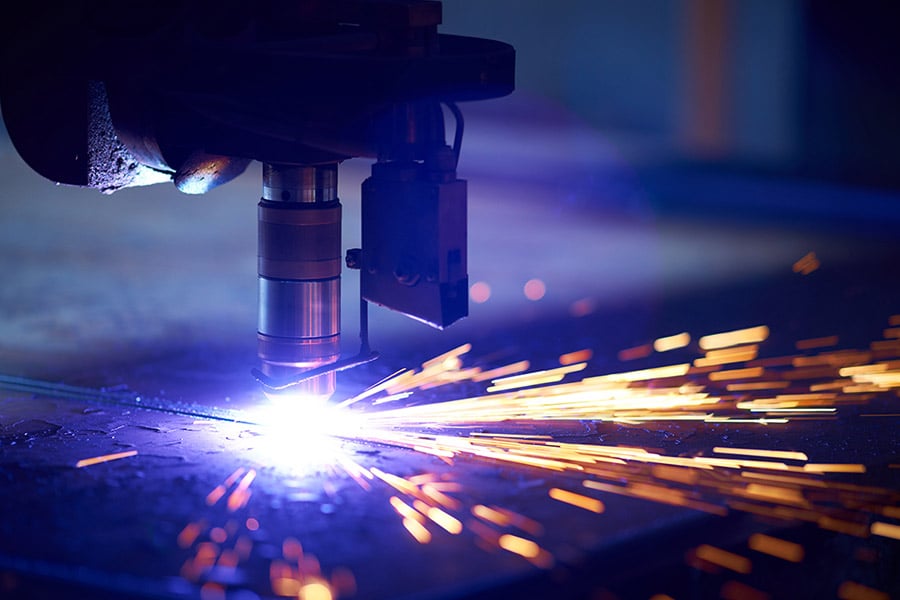
A typical servo system consists of three main components: A servo motor with one or more feedback devices such as a hall effect sensor, encoder, or resolver, a drive amplifier that powers and controls the motor, and the required cabling between the motor and drive. The system as a whole works by means of a series of embedded control loops.
As the drive powers the motor, the feedback devices monitor the rotor’s velocity and/or position. These signals are sent to the control circuits in the drive, which continuously adjusts the current and voltage being supplied to the motor to instantly correct any errors and ensure that the programmed motions are carried out flawlessly.
There are many types of servo motors, but all share the ability to integrate with feedback devices and respond precisely to position, speed and velocity commands from the drive. This variable and precise motion is essential for use in a wide range of industrial applications: robotics, aerospace, medical imaging, laboratory automation, food & beverage production, metal forming, and many more.